Step 1 Install & Configure Tor:
First Install Tor Launcher On Linux
Type Following Command
sudo apt install torbrowser-launcherthen install tor browser via tor browser launchernow open new terminal and type following command sudo apt-get install tor
Step 2 Host a Server:
now open new terminal and type following commands one by one
mkdir tor_service
cd tor_service python3 -m http.server --bind 127.0.0.1 8080To make testing the server easier, it may be useful to create an "index.html" file in the directory from which the server is being run. In a new terminal, in your Tor directory, create the file.
Open New Terminal And Type following command
touch index.html Now we need to edit html file type following command nano index.html Now copy following lines and paste in the editor <html>
<body>
ZTech
</body>
</html> Now save it by pressing ctrl+s and then press ctrl+x With our local server environment configured and available at
127.0.0.1:8080, we can now start to link our server to the Tor network Step 3 Create a Hidden Service:
First, we will need to install or confirm that the Tor service/daemon is installed. The standalone Tor service is an active separate of the Tor Browser package. For Linux/Unix, it's available here. On Ubuntu or Debian-based distros with apt package management, the following command should work assuming Tor is in the distro's repositories.
~/tor_service$ sudo apt install tor
To confirm the location of our Tor installation and configuration, we can use whereis.
~/tor_service$ whereis tor
This will show us a few of the directories which Tor uses for configuration. We're looking for our "torrc" file, which is most likely in /etc/tor. We can move to that directory with cd, as we run the command below.
~/tor_service$ cd /etc/tor/
Finally, confirm that "torrc" is present by simply running ls.
~/etc/tor$ ls
torrc torsocks.conf
torrc torsocks.conf
If the torrc file is present, we will want to edit it. We can use Vim, emacs, or simply GNU nano to edit the file. To edit the file in nano, simply run the following in the terminal. If you're root, you can skip the sudo.
~/etc/tor$ sudo nano torrc In the file, we're looking for the section highlighted below. To find it quickly, use Control-W to search for "location-hidden," hit Enter, and you should jump right to it.
To direct Tor to our hidden service, we'll want to un-comment two lines.
Write the changes with Control-X, type Y, then Enter to exit.
Step 4 Test the Tor Service:
With the changes written to our torrc file and a server running at
127.0.0.1:8080, making our server accessible over Tor is as simple as
starting the Tor service. We can do this from the command line by typing
the following.
Upon starting Tor for the first time with our new configuration, an
.onion address will be generated automatically. This information will be
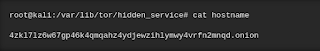
stored in "/var/lib/tor/hidden_service" (or another directory if
specified in the torrc file). First, in a new directory, if you're not a
root user, get root permissionsThe string ending in .onion is our new hidden service address! While this one was automatically generated, we'll be able to customize it later to our preference.
We can test that our service is accessible by opening it in Tor Browser. If the address resolves to your server, you've successfully hosted a hidden service!
Now the .onion string is adress of your website paste it on tor browser and boom you are done
Thanks For Reading :)









3 Comments
Thanks
ReplyDeleteWelcome
Deletenice tutorial
ReplyDelete